Now, almost 10 years after it first announced its system, Toyota has started field tests of a setup that lets it use a variety of very different batteries in one storage system. Curiously, it's not being implemented at a Toyota location. Rather, it is being tested by crosstown rival Mazda, at the company's plant in Hiroshima, Japan.
"Sweep" Lets All Batteries Work Together
It's called the Sweep Energy Storage System, and the sweep function is the key to how it works. It is a device that can switch power flow on and off through connected batteries in microseconds. With sweep, the system doesn't need to have identical batteries. They can be different chemistries, different capacities, and have other differences that might not otherwise be compatible. Other systems, like Tesla's Powerwall, use identical and new battery cells in their packs.
Being able to use whatever batteries you have makes it easier and cost-effective to create stationary power storage. It's like being able to easily combine a watch battery, some AA-cells, and that old phone power pack that's been sitting in your desk.
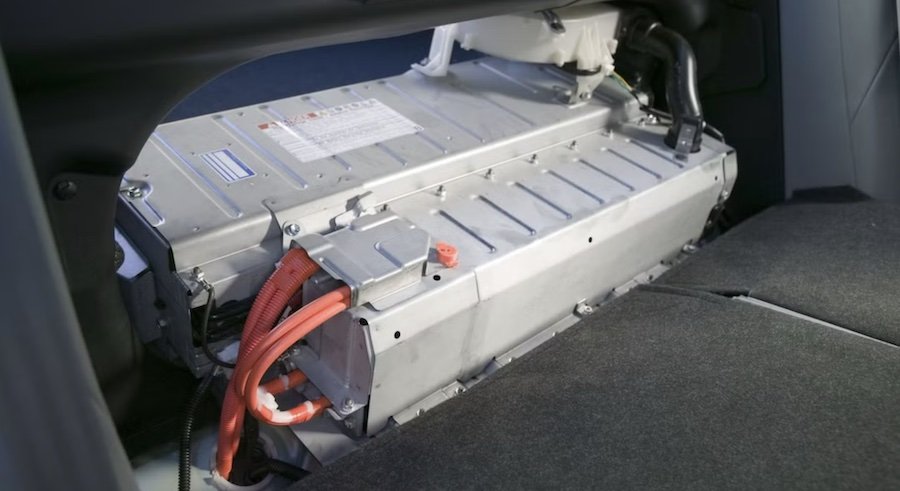
Got a battery pack from an old Prius and one from a newer bZ? No problem. Have 200 packs from different Prius models, all with different capacity capabilities? It can handle that too. No matter how deteriorated individual cells are, it can use them at the maximum capacity of each one. Even old 12V lead-acid batteries can be used, greatly expanding the available supply.
Sweep also allows AC output from the packs using their existing onboard inverters. It doesn't need a separate power conditioner, which cuts costs and improves efficiency.
The point of the system is to store green energy for when you need it. Generate excess solar in the day and store it for use at night. Energy storage is key to making most forms of green energy work.
Grid Will Store Mazda's Solar-Generated Power
Mazda's main factory in Hiroshima is a sprawling facility in the city. It's also home to the only automaker-operated power generation system in Japan. Mazda has installed 1,500 MWh of solar generating capacity on the roof of the plant, which is also the building where it charges batteries for its MX-30 EV. That's enough power to run a medium-sized village.
The storage test will use batteries taken from electrified vehicles to regulate supply and demand of the solar power, helping balance out fluctuations from usage and weather. Toyota's release said that energy storage via a battery ecosystem is one of the seven mobility industry issues Japanese auto manufacturers are trying to address. This one is meant to support building a more resilient supply chain and stable procurement of resources.
In 2022, Toyota announced that it planned to add 100,000 kWh of supplied electricity by the mid-2020s at a thermal power station in Yokkaichi, closer to its Toyota City home. This latest announcement suggests that plan has not been implemented on time.
Related News